Search
- Page Path
- HOME > Search
Original Article
- Clinical Study
- Fasting and Postprandial Hyperglycemia: Their Predictors and Contributions to Overall Hyperglycemia in Korean Patients with Type 2 Diabetes
- Jaecheol Moon, Ji Young Kim, Soyeon Yoo, Gwanpyo Koh
- Endocrinol Metab. 2020;35(2):290-297. Published online June 24, 2020
- DOI: https://doi.org/10.3803/EnM.2020.35.2.290
- 6,888 View
- 201 Download
- 5 Web of Science
- 5 Crossref
-
 Abstract
Abstract
 PDF
PDF PubReader
PubReader  ePub
ePub - Background
This study aimed to identify factors that affect fasting hyperglycemia (FHG) and postprandial hyperglycemia (PPG) and their contributions to overall hyperglycemia in Korean patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
Methods
This was a retrospective study conducted on 194 Korean T2DM patients with 7-point self-monitoring blood glucose (SMBG) profiles plotted in 4 days in 3 consecutive months. We calculated the areas corresponding to FHG and PPG (area under the curve [AUC]FHG and AUCPPG) and contributions (%) in the graph of the 7-point SMBG data. The levels of glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were categorized by tertiles, and the contributions of FHG and PPG were compared.
Results
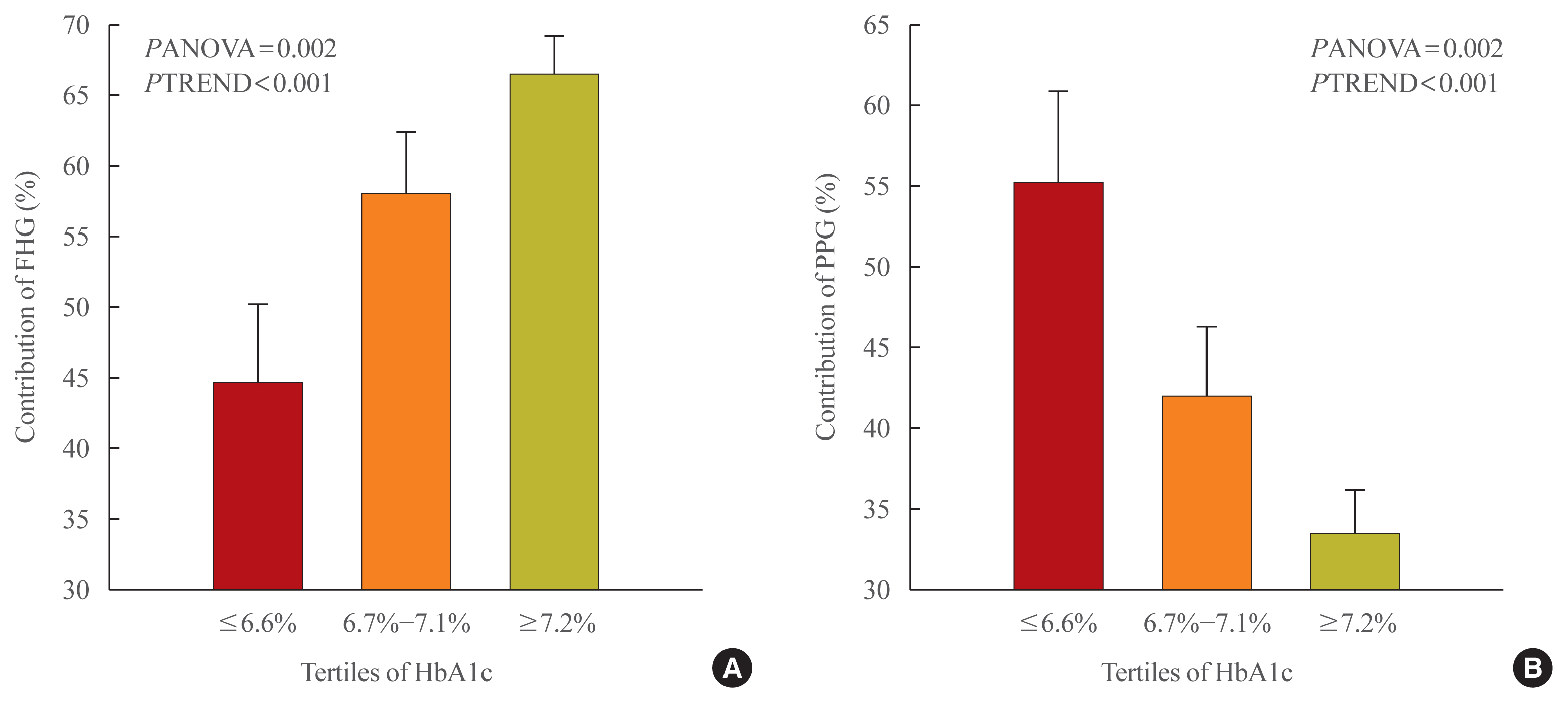
The relative contribution of FHG increased (44.7%±5.6%, 58.0%±4.4%, 66.5%±2.8%; PANOVA=0.002, PTREND <0.001), while that of PPG decreased (55.3%±5.5%, 42.0%±4.4%, 33.5%±2.8%; PANOVA=0.002, PTREND <0.001) with the elevated HbA1c. Multivariate analysis showed that HbA1c (β=0.615, P<0.001), waist circumference (β=0.216, P=0.042), and triglyceride (β=0.121, P=0.048) had a significant association with AUCFHG. Only HbA1c (β=0.231, P=0.002) and age (β=0.196, P=0.009) was significantly associated with AUCPPG.
Conclusion
The data suggested that in Korean T2DM patients, FHG predominantly contributed to overall hyperglycemia at higher HbA1c levels, whereas it contributed to PPG at lower HbA1c levels. It is recommended that certain factors, namely age, degree of glycemic control, obesity, or triglyceride levels, should be considered when prescribing medications for T2DM patients. -
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by- Prospective study of the association between chronotype and cardiometabolic risk among Chinese young adults
Tingting Li, Yang Xie, Shuman Tao, Liwei Zou, Yajuan Yang, Fangbiao Tao, Xiaoyan Wu
BMC Public Health.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Effects of mulberry twig alkaloids(Sangzhi alkaloids) and metformin on blood glucose fluctuations in combination with premixed insulin-treated patients with type 2 diabetes
Ziyu Meng, Chengye Xu, Haoling Liu, Xinyuan Gao, Xinyu Li, Wenjian Lin, Xuefei Ma, Changwei Yang, Ming Hao, Kangqi Zhao, Yuxin Hu, Yi Wang, Hongyu Kuang
Frontiers in Endocrinology.2023;[Epub] CrossRef - Evaluating Triglyceride and Glucose Index as a Simple and Easy-to-Calculate Marker for All-Cause and Cardiovascular Mortality
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, You-Cheol Hwang, Hong-Yup Ahn, Cheol-Young Park
Journal of General Internal Medicine.2022; 37(16): 4153. CrossRef - A new approach for investigating the relative contribution of basal glucose and postprandial glucose to HbA1C
Jing Ma, Hua He, Xiaojie Yang, Dawei Chen, Cuixia Tan, Li Zhong, Qiling Du, Xiaohua Wu, Yunyi Gao, Guanjian Liu, Chun Wang, Xingwu Ran
Nutrition & Diabetes.2021;[Epub] CrossRef - The Clinical Characteristics of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus in Korea: A National Health Information Database Study
Kyung-Soo Kim, Sangmo Hong, Kyungdo Han, Cheol-Young Park
Endocrinology and Metabolism.2021; 36(3): 628. CrossRef
- Prospective study of the association between chronotype and cardiometabolic risk among Chinese young adults


 KES
KES

 First
First Prev
Prev



